An authoritative DNS server is responsible for responding to queries about domain names within its zones with definitive data stored. These servers do not cache query results but use data saved directly in their system. This data can originate from either a primary (master) or secondary (slave) server.
Types of Authoritative DNS Servers
Primary DNS Server (Master): Holds the authoritative copy of all zone records. The DNS administrator updates the master server’s zone records. All updates are automatically synchronized to slave servers using the DNS protocol.
Secondary DNS Server (Slave): This server maintains an exact replica of the master server. It distributes DNS query loads and enhances the availability of DNS zones, ensuring continued functionality in case the primary server fails.
Differences Between Authoritative and Recursive DNS Servers
Authoritative DNS Servers:
- Provide final answers to queries directly from their stored data.
- Answer types include authoritative DNS information, authoritative NXDOMAIN (non-existent domain), and authoritative empty NOERROR (valid domain but no data).
- Direct queries to other nameservers if they do not have the answer.
Recursive DNS Servers:
- Serve as intermediaries that fetch data from other servers to respond to DNS queries.
- Cache information to speed up future queries.
- Types of answers include cached authoritative data, cached non-authoritative data, and data retrieved from authoritative servers.
Аuthoritative DNS server
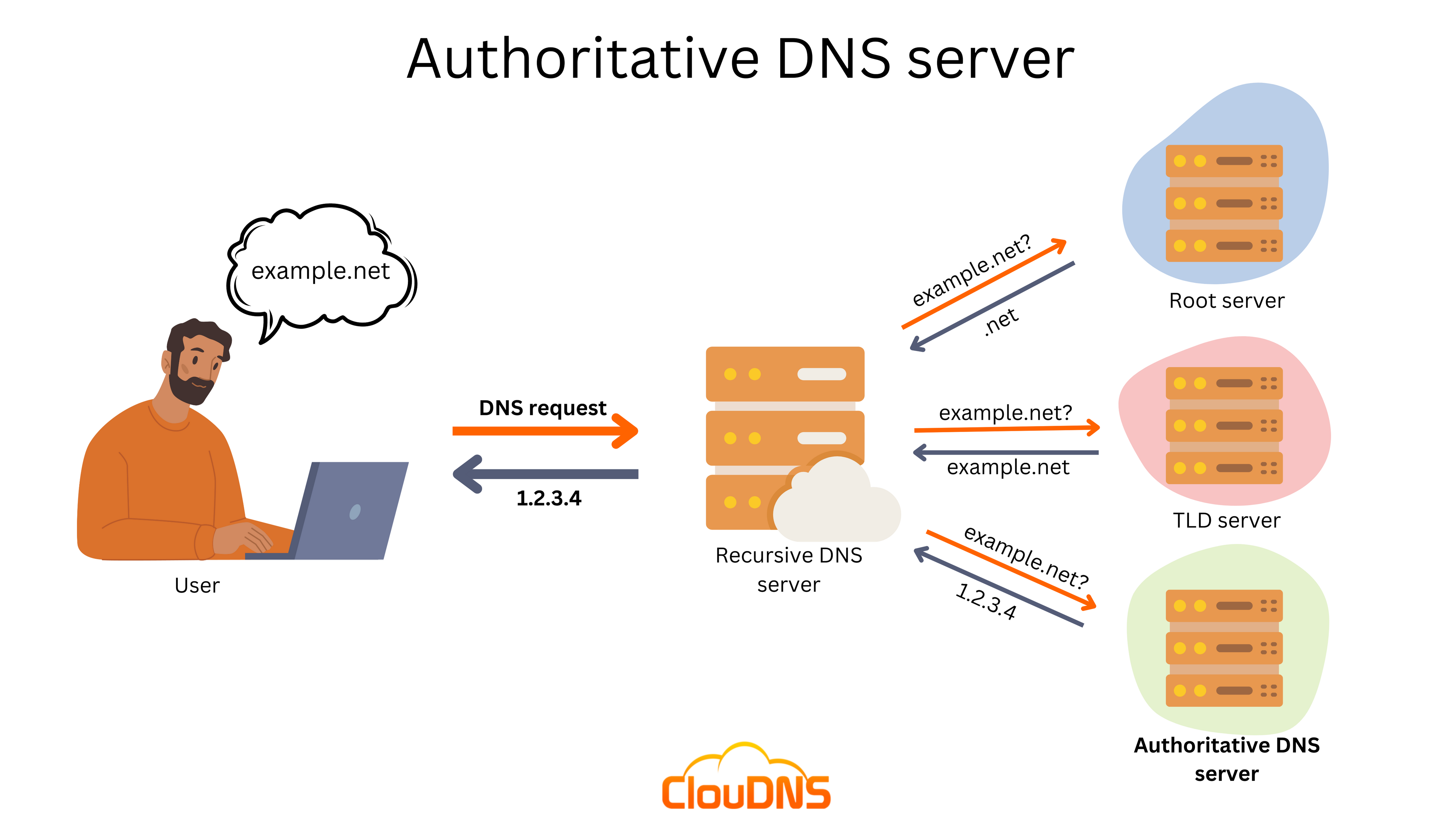
An Аuthoritative DNS server is responsible for answering DNS queries for a particular set of DNS zones by providing information from its own data. It does not have the need to reference another source. Most commonly, it replies to the requests with one of the following types of answers:
- Authoritative DNS information (DNS records) from its own store. It could come from a master zone file, a secondary zone duplicate transferred from a master server, Dynamic DNS, etc.
- In case it doesn’t know the answer, it is going to direct to another nameserver. For instance, the Root name server points to the responsible TLD (Top-Level Domain) server.
- An authoritative NXDOMAIN. It replies that the requested domain name doesn’t exist.
- An authoritative empty NOERROR (NODATA) answer. The requested domain name exists, but the particular queried DNS record does not.
Recursive DNS server
The Recursive DNS server replies to DNS queries by asking other nameservers for the needed information (DNS records). In some cases, this server responds to DNS requests directly from its cache if the information is available there. In case it is not, the Recursive DNS server, also known as DNS resolver, is going to perform a search and ask the responsible authoritative servers until it finds the needed answer.
Normally, Recursive DNS servers store information about previously queried domain names in their cache memory for further use. This reduces network traffic and improves performance.
Recursive DNS servers normally answer DNS queries in the following way:
- Authoritative DNS information (DNS records) from its own store, if there is any. That could be a positive response, NXDOMAIN, or NOERROR/NODATA.
- Non-authoritative DNS information that is received and cached from a previous recursive DNS query, if there is any.
- Data retrieved from remote authoritative name servers. It can be further cached and reused for answering future DNS queries.
Recursive DNS servers are most commonly used to reply to general DNS queries for users on a local network.
How to Find the Authoritative DNS Server for a Domain
You can discover which DNS servers are authoritative for a domain using several command-line tools:
Dig Command:
bashCopy codedig +short NS exampledomain.com
NSlookup Command:
bashCopy codenslookup -type=NS exampledomain.com
Host Command:
bashCopy codehost -t NS exampledomain.com
WHOIS Command:
bashCopy codewhois exampledomain.com | grep -i “Name Server:”
Replace “exampledomain.com” with the domain you are querying.
Importance of Authoritative DNS Servers
Authoritative DNS servers are crucial for:
- Resolution: Translating domain names to IP addresses, enabling access to websites and services.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Maintaining up-to-date and accurate records.
- Performance: Optimizing the speed of DNS resolutions across global networks.
- Security: Reducing vulnerabilities to DNS spoofing and DDoS attacks.
- Domain Management: Allowing administrators to update and manage DNS records efficiently.
Best Practices for Managing Authoritative DNS Servers
- Redundancy: Utilize multiple servers across diverse locations to ensure reliability and reduce risks of downtime.
- Security Measures: Implement DNSSEC to safeguard against DNS threats.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor the servers for any operational issues or security threats.
- Capacity Planning: Ensure the infrastructure can handle expected query volumes and potential growth.
Premium DNS Service by ClouDNS
ClouDNS offers robust Authoritative DNS Server solutions. Check our Managed DNS page for details. Our services include:
- Cloud-based infrastructure with over 50 points of presence.
- Advanced features like E-mail Forwarding, Web Forwarding, Dynamic DNS, Domain Parking, HTTP REST API, DNS statistics, zone sharing, and more.
- Comprehensive protection against DDoS attacks.

Tech Enthusiast & Knowledge Sharer
I am a passionate technologist dedicated to demystifying the world of networking, cloud computing, and automation. Focusing on simplicity and practicality.
I believe in breaking down complex concepts into understandable and actionable insights.